Intent-based transactions are emerging as one of the most important upgrades to how users interact with blockchain networks. Instead of manually executing complex steps, users can simply express what they want to achieve, and the system figures out how to execute it efficiently and securely.
In this beginner guide, we explain what intent-based transactions are, how they work, why they matter for the future of crypto, and everything else you need to know.

Making a deal in the early days of decentralized finance (DeFi) was similar to solving a riddle. You had to calculate the gas costs, pick the best route for your trade, and pray the deal went through. You lost money if you made a mistake.
To address this and increase DeFi’s accessibility, intent-based transactions were created. The system functions like a taxi driver; you simply tell it where you want to go, and it takes care of the driving, rather than giving you a box of tools and instructing you to build the automobile.
What Are Intents?
An intent is your objective in DeFi. Therefore, an intent just expresses the intended result (e.g., “I want X, and I am willing to pay Y”), in contrast to a normal transaction that contains detailed instructions (e.g., “Do A, then B, to get C”). Let’s contrast the more recent intent model with the conventional approach.
The Traditional Method: Imperative
This is the “Do It Yourself” method. The blockchain needs precise instructions.
- Illustration: “Take my token, go to this specific pool, swap it, pay this much gas, and send the new token to my wallet.”
- Concern: Your transaction fails if the pool is empty or the gas fee changes. You must be fully aware of how the system operates.
The Newer Method: Declarative Intent
This is the “Make It Happen” strategy that we previously discussed. You concentrate on the outcome.
- Illustration: “I want at least 2,000 USDC, and I have 1 ETH.” Make it happen.
- Concern: You don’t give a damn about how the gas is paid for or which pool is used. All you want is for the outcome to fulfill your request.
What Are Intent-Based Transactions?
An intent-based transaction allows a user to specify a desired outcome rather than submitting a traditional transaction with fixed parameters.
Instead of saying:
“Send this transaction with exact gas, route, and execution steps”
The user says:
“Swap ETH to USDC at the best possible price”
“Bridge funds to Arbitrum cheaply”
“Buy this NFT below a certain price”
The system then determines the optimal way to fulfill that intent.
How Do Intent-Based Systems Work?
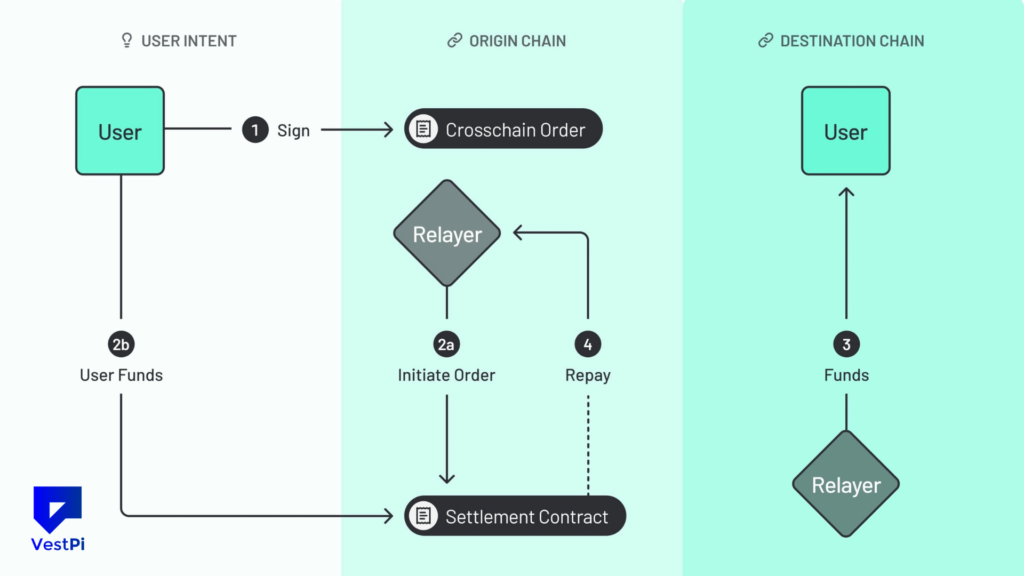
The transaction lifetime in an intent-centric architecture differs greatly from the conventional public mempool paradigm.
- User expression: The user signs a statement (the purpose) outlining their precise objective, such as exchanging Token A for Token B at a minimum cost.
- Outsourcing: A network of outside agents, sometimes referred to as fillers, searchers, or solvers, receives this intent.
- Execution: To determine the best course of action, solvers compete. To satisfy the request, they can combine liquidity from other sources, batch several orders, or use their own inventories.
- Settlement: The transaction is carried out on-chain by the successful solver. In many designs, the trade reimburses the solver for the upfront gas costs.
Benefits of Intent-Based Transactions?
1. Improved User Experience (UX)
Intents abstract the technical complexity of DeFi. Users do not have to worry about gas surges, failed transactions, or manually bridging assets between chains. For example, “gasless” trading is made feasible by solvers paying network fees in the native coin (such as ETH) while the user pays in the token being swapped (such as USDC).
2. MEV Protection
Traditional traders are subject to Maximal Extractable Value (MEV) tactics, such as front-running and sandwich attacks. Intent-based systems frequently safeguard users by transferring the execution risk to solvers. Because the deal is not finalized until the user’s criteria are met, the solution has an incentive to protect the trade’s value.
3. Capital Efficiency and Better Pricing
Users can access a competitive market of solvers who look for the best pricing across both on-chain and off-chain liquidity sources by outsourcing execution. In order to increase efficiency and lessen the overall burden on the network, solvers can also batch numerous transactions together (coincidence of wants).
Examples of DeFi Platforms With Intent-Based Transactions
To improve their services, some DeFi protocols have embraced intent-based models:
- CoW Protocol: Matches trades and shields users from MEV using batch auctions.
- UniswapX: Uses a Dutch auction system to aggregate liquidity from many sources and provide gas-free swaps.
- 1inch Fusion: Enables customers to place orders, which are carried out by qualified resolvers who cover the cost of gas.
- Across Protocol: Makes use of intents for quick and economical cross-chain bridging.
Risks and Challenges
Although intentions make life easier, there are a few things to be aware of:
- Centralization Risk: It’s now difficult to become a solver. The system tends to become less decentralized if only a few large corporations can accomplish it.
- Trust: You must have faith that the system of solvers is operating equitably. Compared to the previous method, it can be more difficult to understand precisely what is happening because some of the work takes place off the main blockchain.
Final Thoughts
Intent-based transactions represent a fundamental shift in how users interact with blockchains. By focusing on outcomes rather than mechanics, crypto becomes more intuitive, more efficient, and more secure.
In general, intent-based transactions are trying to make DeFi as easy as using a regular banking app. As this technology evolves, we can expect smoother, cheaper, and safer trading for all levels of DeFi users.
For beginners, intent-based transactions remove friction, and for advanced users, they unlock powerful automation. As infrastructure matures, intent-based execution will likely become the default interaction model for crypto applications.



