Individuals and businesses can use public and private networks to achieve their aims. In this article, you will learn about the blockchain private key QR code, differences between public and private blockchains, use cases, other types of blockchains, and how organizations can best leverage each to support strategic goals.

What Is a Blockchain and How Does It Work?
A blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely and openly documents transactions. It runs on a peer-to-peer computer network and is decentralized, meaning it is not governed by a central authority.
Every block in the chain has a hash, which is similar to a distinct digital fingerprint that links it to the preceding block and represents a particular piece of information, making the chain of blocks practically impenetrable.
The blockchain’s network of nodes, or computers, verifies each transaction as it happens. The transaction is recorded as a new block on the chain when it has been verified. Because every node on the network has a copy of the blockchain, there is never a single point of failure, and everyone has access to the same data.
The security of blockchain is one of its main benefits. It is very impossible to change or manipulate any earlier transaction data without the network noticing since each block in the chain is connected to the one before it.
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A transparent, safe, and decentralized method of documenting transactions on a digital ledger is through a public blockchain. It offers a robust framework for developing decentralized services and apps that are available to anybody with an internet connection.
Anyone can view the data, join the network, and take part in the validation of transactions. Dock, Bitcoin, and Ethereum are a few instances of public blockchains.
What Are the Advantages of a Public Blockchain?
1. Accessibility
Public blockchains are available to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of geography or background. This results in a more inclusive and open environment, in which anybody can join the network and profit from its applications.
2. Innovation
Public blockchains promote innovation by allowing developers to create new applications and services that take advantage of the network’s capabilities. This has resulted in the development of a diverse spectrum of decentralized applications, including digital identification and supply chain management solutions.
3. Security
Public blockchains use powerful cryptographic techniques to secure and authenticate transactions, and they operate on a decentralized network. These characteristics make them highly secure and resistant to attacks, as any effort to alter or manipulate data on the network is noticed by the other nodes.
The more participants a blockchain has, the more secure it is. As more users join the network, the number of nodes that validate each transaction grows. This makes it more difficult for a single malicious actor to manipulate the network because a successful attack requires control of the majority of the nodes.
4. Transparency
The transactions that take place on the network are visible and verifiable to anybody. Because everyone connected to the network can view the same information, this fosters a high level of trust and accountability.
Common Misconceptions About Public Blockchains
Since sensitive data can be viewed by anybody, there is a widespread misconception that public blockchains are insecure. Nonetheless, the following strategies can effectively safeguard data:
- Data encryption is necessary before storing sensitive information on the blockchain. However, since sensitive data is typically housed off-chain, Dock does not employ this technique to maximize data security.
- A link and/or a cryptographic hash (such as a digital fingerprint) of the data may be included if sensitive information is kept off-chain. Issuing credentials like driver’s licenses, school degrees, and identity documents as Verifiable Credentials is one way to secure data connected to a blockchain.
- Verifiable credentials are a kind of digital document that enables people and organizations to securely and decentralizedly demonstrate their identity, credentials, and claims.
- Users can verify their details to verifiers without providing any personal information at all if a Verifiable Credentials provider has Zero-Knowledge Proof technology features. For example, they can verify their age without providing their date of birth or confirm that they reside in a city that qualifies for a government program without disclosing their address.
Use Case of Public Blockchains
Few people are aware of the increasing number of use cases for public blockchains because, up until now, cryptocurrencies have dominated their use. Public blockchains offer a decentralized, transparent, and safe platform for many different industries and applications, such as government, healthcare, and banking.
1. Healthcare
With express authorization, public blockchains can allow patients and healthcare professionals to safely share electronic health records while protecting patient confidentiality and privacy. Additionally, patients will be able to see who has accessed their data and why, which would boost openness and confidence in the medical system.
2. Finance
By increasing traceability and transparency throughout medical supply chains, public blockchains can lower the danger of counterfeit goods and enhance patient safety. For instance, tracking the transfer of pharmaceuticals and medical equipment from the producer to the final consumer might be done via a public blockchain.
Additionally, public blockchains can be utilized to verify digital identities and enhance client data protection while maintaining transparency. For instance, client DIDs that are granted as Verifiable Credentials, such as driver’s licenses and government-issued ID documents, might be stored on a public blockchain to facilitate quick ID verification.
By securely transferring money across borders, public blockchains can lower the risk of fraud and boost confidence in the financial system. The transfer of money between banks or other financial institutions, for instance, might be documented and verified using a public blockchain. This would enable the transfer process to be more transparent and accountable.
3. Government
Passports and driver’s licenses are examples of identity documents that can be safely issued and verified using public blockchains. People have complete choice over when and with whom they choose to release their information, thanks to Verifiable Credentials and DIDs. Their information cannot be accessed by credential verifiers without their express authorization.
Public records like birth certificates, property deeds, and identity documents can be issued by governments as Verifiable Credentials, which individuals can safely retain on their digital wallet.
A bank giving a loan might send a QR code to the borrower in order to request different credentials, such as a full name, date of birth, and work pay, if, for instance, a real estate transaction calls for new credentials.
What Is a Private Blockchain? (AKA Permissioned Blockchain)
A private blockchain is a decentralized ledger that is exclusively available to a limited number of people or businesses. It has a single operator or entity that manages network access, information viewing, and blockchain data creation.
People must accept an invitation, confirm their identity, or supply the required data in order to access a private blockchain network.
In contrast to public blockchains, where users’ identities are mostly anonymous, private blockchain users’ identities are known. Corda and Hyperledger are two instances of private blockchains. The owner can override, modify, or remove entries on the blockchain as they see fit, but only specific users are allowed to maintain the shared ledger.
Smart contracts or other automated techniques are used by the network operator or operators or a protocol that has been accepted by the network to authenticate and validate the participant’s information.
On a private blockchain, a transaction is sent to the network for validation. The transaction is posted to the blockchain as a new block once the nodes have verified it.
Why Some Organizations Use Private Blockchains
A private blockchain, as opposed to a public blockchain, is a closed database that employs encryption to guarantee security and adhere to organizational regulations. Many organizations utilize this option to keep part or all of their transactions private or solely for internal uses.
Efficiency and immutability are given precedence over user identity protection and transparency in private blockchains. They can process more transactions since it takes less time to reach a consensus to validate a transaction when there are fewer users in the centralized network.
Disadvantages of Private Blockchains
1. Security Risks
Since there are fewer nodes (computers) in the controlled network, private blockchains are far more susceptible to security threats than public blockchains, despite being more secure than traditional databases. A hacker can alter data or stop transactions if they manage to get access to a private blockchain.
2. Lack of Transparency
Private blockchains are opaque because they favor privacy. It may be challenging to confirm the veracity and correctness of the data on the blockchain due to this lack of transparency.
3. Cost
Since private blockchains need a certain amount of processing power and data storage, they can be costly to set up and maintain. Consequently, the expenses will increase as the volume of data increases. On the other hand, with public blockchains, the costs are split among all node operators, and the rewards pay for the expenses.
4. Centralization
Private blockchains are frequently centralized, meaning that the network is managed by a single company. Since decentralization is one of the core ideas of blockchain technology, this concentration may be problematic.
The Difference Between Public and Private Blockchains
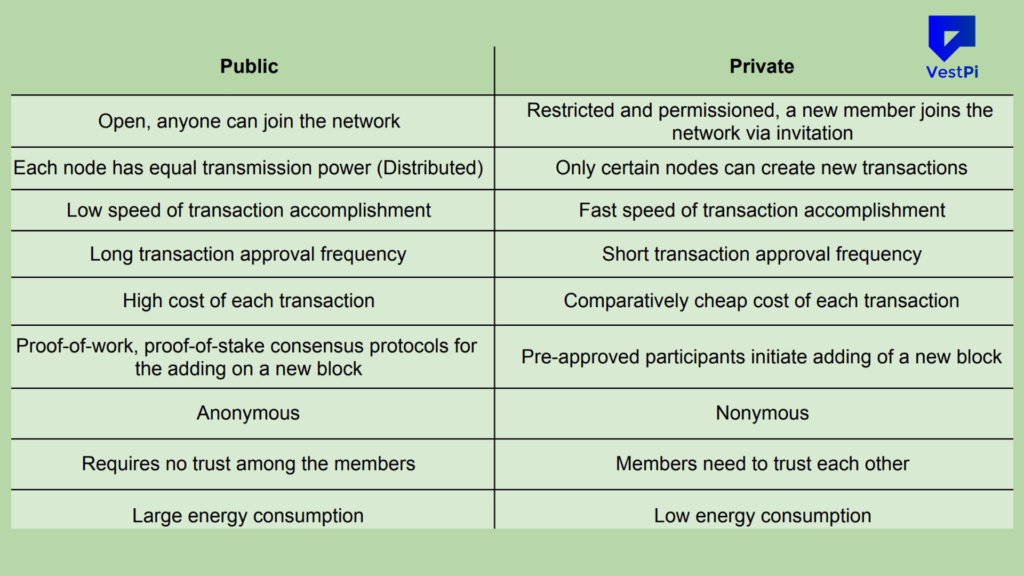
Before going further, here is a summary of between these two major types of blockchains.
| Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain | |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Anyone is free to join and participate in the core activities of the blockchain network including reading, writing, adding blocks, and auditing the network’s activities. | Only selected and verified participants can join the network. |
| Control | Decentralized and managed by a community of users with no single point of control. Once blocks are validated, entries can’t be edited or deleted. | Centralized and controlled by a single entity or organization. The operator has the rights to override, edit, or delete entries on the blockchain. |
| Transparency | Transparent as all transactions are visible to anyone on the network. | Private as only authorized users can view the data and transactions on the network. |
| Anonymity | Users can remain anonymous. | The identities of people involved in the transaction are known. |
| Data Visibility | All transactions are visible on the network. | Access to the network is restricted and controlled. |
| Security | Highly secure and resistant to attacks, due to the decentralized nature of the network and use of cryptography | Secured with the use of cryptography |
Other Types of Blockchains
1. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain is a kind of blockchain that incorporates aspects of both private and public blockchains. Depending on the use case and application, it permits a combination of restricted and open network access.
For instance, a business might store its data on a private blockchain to maintain confidentiality while adding a digital fingerprint to a public blockchain to ensure security. The data on the private blockchain and the public blockchain fingerprint can be compared if someone wishes to look into the possibility that the data was altered.
2. Consortium Blockchain (AKA Federated Blockchain)
A consortium blockchain is a kind of blockchain in which several organizations or groups collaborate to create a network, with each member playing a part in the network’s transaction recording and verification.
This is different from public blockchains, where anybody can join the network, and private blockchains, where a single entity controls the network.
Every member of a consortium blockchain has an equal voice in how the network is run and governed. Before a transaction is uploaded to the blockchain, all participants must concur that it is legitimate. This process is used to verify and record transactions.
This preserves a certain level of control and privacy for the users while guaranteeing that the network is safe, transparent, and impenetrable.
What Is a Blockchain Private Key?
A blockchain private key is a cryptographic key that enables users to access and control their digital assets on the blockchain. It is a long sequence of alphanumeric characters that is unique to each user. Private keys are used to sign transactions, enabling users to transmit and receive digital assets.
What Is a Blockchain Private Key QR Code?
A blockchain private key QR code is a code containing a user’s private key. Since it removes the need to manually enter private keys, it is a practical method of managing and storing them. QR codes can be detected and scanned by most types of smartphones and PCs, making them easy to use.
How to Use a Blockchain Private Key QR Code Safely
When utilizing a blockchain private key QR code securely, bear the following in mind:
- Scan QR codes only from reliable sources. QR codes from unidentified sources should not be scanned since they can contain dangerous code.
- Keep your QR code in a safe place. After scanning a QR code, put it somewhere safe, such as, a password-protected file, or a hardware wallet.
- Keep your QR code private. The sensitivity of your private key QR code is equal to that of your private key. Never provide it to anyone, even if they say they work for a reputable company.
The Bottom Line
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we store and transmit sensitive data. There are two major types of blockchains: public and private. Public blockchains offer more accessibility, innovation, security, and transparency, while private blockchains provide more control and privacy.
Additionally, storing and managing private keys is made easy and safe with blockchain private key QR codes. But it’s crucial to utilize them securely and only scan QR codes from reliable sources. You may assist prevent unwanted access to your digital assets by heeding the above advice.



