While L2s are essential for faster onchain interactions, understanding Arbitrum vs Optimism differences is crucial for DeFi users and developers. Ethereum’s Merge solved its energy problem, but it has reframed scalability as a top challenge in blockchain today. This has prompted Layer 2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum (among many others) to step in to aid Ethereum’s scalability journey.

Overview of Optimism vs. Arbitrum
Both Optimism (also known as “OP”) and Arbitrum are Ethereum Layer 2s. While “Layer 2” may be a jargon, understanding what it implies in practical terms is critical.
Simply put, Layer 2 solutions are protocols developed on top of a blockchain, like Ethereum, to assist grow the network. L2s perform transactions off the Ethereum mainnet, reducing congestion, gas prices, and improving transaction speed, making Ethereum more efficient and accessible to users and developers.
This enables Ethereum to process more transactions per second (TPS) and provide a more fluid user experience, particularly during times of heavy demand. While both Optimism and Arbitrum are intended to increase Ethereum’s capabilities, they work in various ways, with significant trade-offs in terms of performance, cost, and ecosystem integration.
These insights can assist DeFi participants in lowering costs, increasing transaction efficiency, and strategically positioning themselves inside the expanding crypto market.
| Optimism | Arbitrum |
| – Founded. 2019, mainnet launched in 2021.- Scalability via Optimistic Rollups + single-round fault-proof system.- Employs Optimistic Virtual Machine (OVM) for Ethereum compatibility.- Superchain-focused, aimed at interlinking the L2 ecosystem | – Founded. 2021, mainnet launched in 2021.- Scalability via Optimistic Rollups + interactive fraud-proof system.- Employs Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) for Ethereum compatibility.- DeFi-centered, with dApps like Uniswap and Synthetix using the network to scale. |
Arbitrum now has a Total Value Locked (TVL) of about $2.4 billion, whereas Optimism has over $430 million. Arbitrum has conducted almost 1.5 billion transactions, indicating widespread acceptance, whereas Optimism has only recently exceeded the 550 million threshold. While both platforms use Optimistic Rollups, they each provide unique features that cater to different demands within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Arbitrum vs Optimism: Technical Comparison
Aside from topline measurements, when we dig deeper into the tech stack, the differences between these two Layer 2 solutions become much more apparent. Both Optimism and Arbitrum promise lower fees and faster transactions in a similar manner. To comprehend their genuine differences, let’s look at the underlying technologies.
Architecture & Network Performance
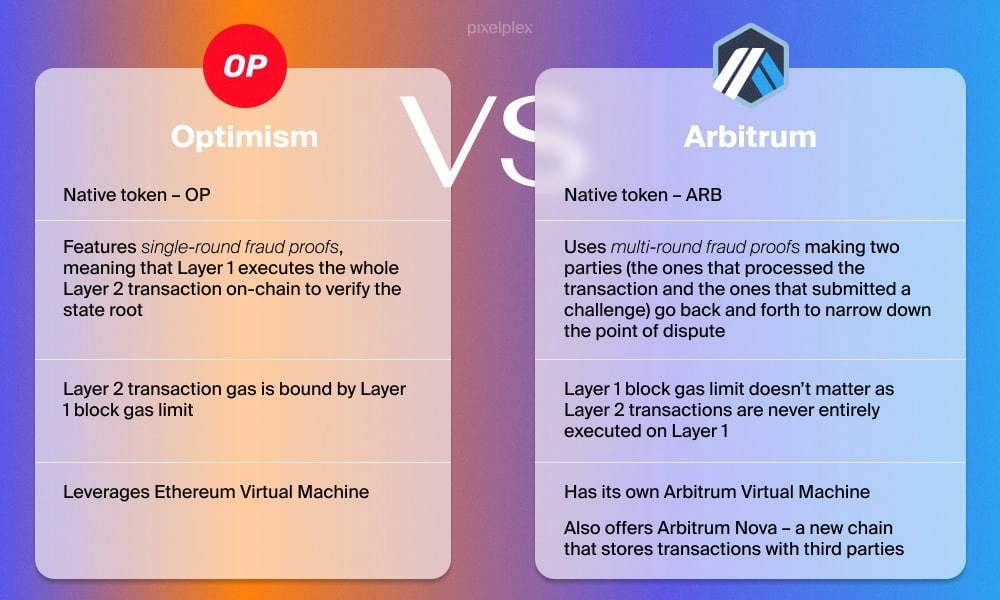
- Optimism is developed with a significant emphasis on Ethereum compatibility. It employs Optimistic Rollups, in which transactions are presumed genuine by default and only verified in the event of a dispute. The OVM enables developers to deploy Ethereum contracts on Optimism with little changes.
- Arbitrum likewise employs optimistic rollups, allowing its AVM to handle Ethereum contracts with comparable efficiency. Arbitrum differs slightly from OP in its use of multi-round interactive fraud-proofing, which reduces dispute costs (more on this in the following section).
Security Models
While both Optimism and Arbitrum leverage Ethereum’s security, they approaches transaction validity differently.
- Optimism employs a single-round fault-proof system, with transactions presumed genuine unless challenged. If a dispute emerges, the system sends the transaction directly to Ethereum’s Layer 1 for verification, resulting in increased mainnet gas fees. This strategy allows for faster finality for the majority of transactions, but resolution of disputes can be more costly.
- Arbitrum uses an interactive technique to prevent fraud across multiple rounds. Rather than instantly escalating disputes to Ethereum, it goes through incremental verification steps to ensure that just the challenged portion of a transaction is eventually submitted to the mainnet. While this strategy increases dispute resolution delays, it saves money by eliminating the requirement for full transaction re-execution on Ethereum.
User Experience of Arbitrum vs Optimism
Our technical analysis shows that both Optimism and Arbitrum strive to increase Ethereum’s transaction capacity. While they both follow a similar concept (albeit with different technological techniques), the most visible variations are at the user level.
Costs & Fees
- Petrol fees on Optimism in 2024 averaged 0.116 Gwei. While Optimism processes transactions rapidly, rollup disputes necessitate the settlement of complete fraud proofs directly on the Ethereum L1, which incurs additional costs due to mainnet gas taxes.
- Petrol fees on Arbitrum in 2024 averaged 0.051 Gwei. Arbitrum’s multi-round fraud-proofing contributes to cost savings and long-term gas economy.
For most customers, Arbitrum’s reduced fees make it the better choice for minimising variable costs, whereas Optimism provides speedier confirmations at the expense of somewhat higher prices in dispute cases.
A quick note: Both Optimism and Arbitrum are completely interoperable with major Ethereum wallets like MetaMask, making it simple for users to connect with Ethereum-based dApps and transfer assets between both L2s.
User Interface
- Optimism features a streamlined UI that is consistent with Ethereum-native applications. It focusses primarily on Ethereum-first connectors, making it an excellent solution for those seeking simple Ethereum interoperability.
- Arbitrum has a well-developed DeFi ecosystem with popular dApps such as Fluid and Radiant. These apps have refined user interfaces because to the network’s widespread use in DeFi.
Network Stability
- While Optimism provides excellent network stability, its fraud-proof method might cause occasional delays in transaction finality, particularly under high congestion. Ethereum’s finalisation process ensures transactions attain hard finality within 13 minutes.
- Arbitrum improves network stability even during peak congestion situations. The hard finality procedure takes approximately 13 minutes, identical to Ethereum’s finalisation time.
Developer Experience of Arbitrum vs Optimism
Unsurprisingly, while Optimism and Arbitrum are both intended to scale Ethereum, they provide robust experiences for developers. The experiences vary slightly in terms of ecosystem acceptance, tooling, and integrations.
Ecosystem Stats
| Optimism | Arbitrum |
| – TVL: ~$430 million- Average transaction speed: ~10.73 TPS- Unique addresses: ~200 million- Partnerships: Chainlink, DIA, Beefy | – TVL: ~$2.4 billion- Average transaction speed: ~20.60 TPS- Unique addresses: ~58 million- Applications: Uniswap, SushiSwap, Aave |
Arbitrum’s larger TVL and richer DeFi integrations make it the leading L2 for financial applications. However, OP’s governance focus and Superchain ambition have led to substantial adoption among protocol developers, including Coinbase’s Base.
Developer Tools and Support
- Optimism offers high Ethereum compatibility, making it a reliable developer tool. While closely aligned with Ethereum’s infrastructure, it may not provide enough flexibility for scalable, high-performance applications.
- Arbitrum provides extensive developer tools, including sophisticated integrations and detailed documentation. The Arbitrum SDK and robust ecosystem support make it a top choice for developers seeking to transition sophisticated dApps to Layer 2.
Optimism vs. Arbitrum: Use Cases

After discussing the benefits and drawbacks of Optimism and Arbitrum for users and developers, we can focus on the use cases that drive these L2 ecosystems. When deciding between the two, it is critical to evaluate your individual requirements or, for developers, the demands of your project.
For DeFi
If you haven’t noticed, Arbitrum has established itself as a major player in the DeFi market. Arbitrum’s huge liquidity and ~460% higher TVL than Optimism (at time of writing) make it an excellent option for traders looking for efficient transaction execution. Here are a couple places to check into for both Optimism vs. Arbitrum.
- Optimism: Synthetix, a derivatives liquidity protocol, uses Optimism, which offers cheaper fees and Ethereum compatibility.
- Arbitrum: GMX, a decentralised perpetual exchange, uses Arbitrum’s scalability to provide efficient trading experiences.
For NFTs
Both Optimism and Arbitrum have been hard at work building their NFT ecosystems to provide users with low-cost alternatives to Ethereum’s mainnet.
- Optimism: Projects like Niftykit offer platforms for minting, managing, and selling NFTs with lower fees.
- Arbitrum: Shift collects listings from key NFT markets to expand Arbitrum’s footprint.
For Gaming
In the gaming industry, where fast transaction throughput and low latency are critical, Arbitrum’s infrastructure has a clear advantage over Optimism. However, both networks provide distinct benefits for various gaming projects.
- Optimism: Dope Wars, a hip-hop-inspired gaming project, uses Optimism, which is compatible with Ethereum.
- Arbitrum: Treasure, the developer of Knights of the Ether and other titles, uses Arbitrum to scale its gaming ecosystem.
For Building
For developers, deciding between Optimism and Arbitrum requires considering tool compatibility, customisation choices, and community support.
Optimism: Provides a development environment that is tightly linked with the Ethereum architecture, allowing for easy deployment of existing Ethereum-based apps.
Arbitrum: Offers a flexible development framework that supports a variety of programming languages and includes tools for custom application creation.
Optimism is more suited for applications that need to integrate seamlessly with Ethereum, whereas Arbitrum is better suited for those that want more flexibility and customisation.
Asset Interoperability of Optimism vs. Arbitrum
Of course, in order to access the OP and Arbitrum ecosystems, you must first cross over to them. And, as the Ethereum L2 paradigm evolves, users’ ability to transfer assets between networks becomes increasingly vital. However, bridging is not always simple. Speed, affordability, security, and compatibility are all relevant considerations.
Bridging Options
Users frequently have two options for moving assets between Optimism, Arbitrum, and many other L2s. The first is through native bridges:
- Brid.gg and Superbridge power the OP ecosystem, while Arbitrum Bridge powers Arbitrum itself. Each supports direct asset transfers between Ethereum and its respective L2s.
- These solutions inherit Ethereum’s security, however withdrawals can occasionally significantly extend the fraud-proof challenge period on optimistic rollups.
Furthermore, there are third-party bridges:
- Protocols like Across enable speedier withdrawals by utilising liquidity pools for rapid swaps.
- These services frequently provide lower prices and more flexibility, enabling customers to connect to various L2s and even alternate ecosystems.
- Across facilitates cross-chain interoperability, making it an efficient alternative for consumers transitioning from Optimism and Arbitrum.
While both Optimism and Arbitrum provide a variety of bridging alternatives, it is crucial to note that bridging prices vary depending on network congestion, bridge architecture, and transaction size.
Security Best Practices
Taking measures when transporting assets is crucial, especially since bridges are a common target for attacks in cryptocurrency. This holds true for interactions with any L2, including Optimism and Arbitrum. When considering bridging, be sure to:
- Prioritise well-audited bridges with solid security track records, such as Across, which has a history of zero occurrences.
- Verify contract interactions before approving transactions to avoid fraudulent approvals.
- Monitor transaction confirmations to ensure that assets arrive safely on the destination chain.
Enhanced Bridging with Across
Users can reliably migrate assets between OP and Arbitrum by selecting the appropriate bridge and adhering to security best practices. Across provides a rapid, secure, and cost-effective means to connect these L2s, allowing users to access the finest possibilities across chains.
Read our entire bridging guidelines for Optimism and Arbitrum to maximise cross-chain compatibility. To get started quickly, here’s a peek at the prices and bridging durations between Arbitrum and Optimism on Across:
- Fill out time and fee estimates for transitioning from Optimism to Arbitrum, and vice versa.
- Actual fill time and fees for moving from Optimism to Arbitrum, and vice versa.
- Fee breakdown for transitioning from Optimism to Arbitrum and vice versa.
Across provides a better solution as the quickest and most cost-effective option to connect assets between Optimism and Arbitrum. Across offers reasonable costs, strong security, and a superior bridging experience at faster rates than usual:
- L1 to L2 takes 15 seconds.
- L2 → L1 takes 10 seconds.
- L2 to L2 time: 3 seconds.
Across can bridge between Optimism and Arbitrum in under two seconds, compared to native bridges that take 15+ minutes and withdrawals that take eight days due to Optimistic Rollup security procedures.
The Future of Optimism vs. Arbitrum

As Ethereum Layer 2 solutions grow, Optimism and Arbitrum pursue distinct ways to improve scalability, interoperability, and decentralisation. Notably, when the wider crypto market adjusts to changing regulatory tides and more institutional onboarding, both Optimism and Arbitrum move correspondingly.
Optimism is driving the Superchain, a network of OP Chains built on the OP Stack to standardise security, governance, and interoperability across different L2s. By 2025, Optimism hopes to improve cross-chain communication with a Message Passing Protocol and ERC-7802, a standard for smooth token bridging between OP Chains.
Arbitrum on the other hand, prioritises customisability and decentralisation, particularly through its Arbitrum Orbit architecture, which allows developers to build custom Layer 3 chains tailored to individual applications.
A significant milestone for 2025 is the decentralisation of its sequencer, which will distribute transaction ordering throughout a larger, decentralised network of participants, lowering the danger of censorship attempts and increasing reliability.
Impact of Ethereum Upgrades
In March 2024, Ethereum’s EIP-4844 upgrade decreased L2 transaction fees and enabled blob-based data availability. Arbitrum’s Nitro update, which optimised transaction compression and data handling, helped them gain an early advantage.
The May 2025 Pectra upgrade improves blob capacity, prices, and scalability across L2s, building on previous advances. Optimism’s Superchain offers cost-effective transactions, but its main advantage is improved cross-chain communication amongst OP Chains through EIP-4844 and Pectra.
Optimism and Arbitrum were early advocates of ERC-7683, the Ethereum standard for expressing cross-chain intents. This standard improves ecosystem interoperability by providing an open-source platform for developers seeking to create protocols and apps with cross-chain capability. ERC-7683 is now supported by over 70 projects (and counting).
Optimism and Arbitrum are likely to continue to play important roles in Ethereum’s long-term scaling strategy. Optimism’s Superchain continues to enable a network of interconnected chains, enhancing crosschain user experiences and establishing a unified L2 ecosystem, whereas Arbitrum’s Layer 3 technology promises to enable developers to create custom, high-performance blockchain solutions for DeFi, gaming, and specialised applications.
Conclusion
As Ethereum’s scaling landscape advances, Optimism and Arbitrum emerge as two key Layer 2 alternatives. Both networks provide faster transactions, reduced fees, and broader accessibility while exploiting Ethereum’s security in unique ways.
On the one hand, Optimism prioritises interoperability and ecosystem unification via the Superchain, resulting in a seamless multichain experience for both developers and users. Arbitrum, on the other hand, prioritises customisation and performance, providing developers with greater freedom via Layer 3 solutions while maintaining significant DeFi acceptance.
Finally, selecting the appropriate L2 is determined by individual demands, and recognising these distinctions enables users and developers to maximise capital efficiency and capitalise on the finest prospects across chains. Both Optimism and Arbitrum are making Ethereum faster and cheaper, albeit in slightly different ways.
However, regardless of whether you trade, stake, or create, you’ll need a dependable mechanism to transport assets between chains. That’s where Across comes in: it bridges your assets faster, cheaper, and without the hassle.